Introduction
In the landscape of nutritional support, enteral and parenteral nutrition stand as two key approaches for supplying crucial nutrients to people who can not fulfill their dietary needs via criterion dental consumption. This article looks into the differences between these two forms of nourishment, shedding light on their definitions, applications, advantages, and training viewpoints. With a growing focus on tailored nutritional support, understanding these distinctions is essential for healthcare professionals, specifically those associated with nursing and allied health.
Understanding the Distinctions Between Enteral and Parenteral Nutrition: A Training Perspective
Enteral nutrition (EN) refers to the shipment of nutrients directly into the gastrointestinal system, typically via a feeding tube such as a PEG (Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy) tube. In contrast, parenteral nutrition (PN) includes carrying out nutrients intravenously, bypassing the digestion system entirely. This basic distinction affects everything from person choice to training demands for healthcare providers.
What is Enteral Nutrition?
Enteral nourishment is created for people who have working digestion systems but are unable to eat food by mouth because of medical problems such as stroke, neurological problems, or dysphagia. EN can be supplied using various approaches:
- Oral Supplements: Nutritional consumes alcohol that supplement meals. Feeding Tubes: Including nasogastric tubes (NG), gastrostomy tubes (PEG), and jejunostomy tubes.
What is Parenteral Nutrition?
Parenteral nourishment deals with people who can not use their intestinal tracts properly due to conditions like digestive tract obstruction or extreme pancreatitis. PN gives total dietary support through:
- Total Parenteral Nourishment (TPN): An intricate blend of carbs, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals supplied directly right into the bloodstream by means of central venous access.
The Relevance of Training in Nutritional Support
As health care comes to be progressively specialized, training procedures are crucial in making certain risk-free and efficient administration of both enteral and parenteral nourishment. Specialized courses like the NDIS PEG Feeding Training and enteral feeding support training courses furnish nurses and assistance workers with necessary skills.

Enteral Feeding Support Training course Overview
This program focuses on:
- Assessing individual needs for enteral feeding. Learning regarding different kinds of enteral formulas. Practical abilities for tube insertion and maintenance.
PEG Training for Nurses
Nurses play a vital function in handling individuals with PEG tubes. Training includes:
- Understanding signs for PEG placement. Techniques for risk-free tube care. Recognizing issues such as infections or blockages.
Comparative Evaluation of Enteral vs. Parenteral Nutrition
|Element|Enteral Nourishment|Parenteral Nourishment|| -------------------------------|--------------------------------------|---------------------------------------|| Path|Intestinal tract|Intravenous|| Indicators|Useful GI system|Non-functional GI tract|| Nutrient make-up|Entire foods/formula|Customized TPN remedy|| Danger aspects|Tube-related issues|Infection risk from IV accessibility|| Expense|Usually lower|Greater as a result of complex formulations|
Benefits of Enteral Feeding over Parenteral Feeding
Preservation of Gut Integrity: EN keeps digestive tract feature by advertising mucosal integrity. Lower Infection Risks: Compared to PN, EN has a reduced risk of infections given that it does not include blood vessel access. Cost-effectiveness: EN generally sets you back much less than PN due to fewer necessary resources.When is Parenteral Nourishment Necessary?
While enteric routes are liked when possible, PN ends up being needed in scenarios such as:
- Severe malabsorption syndromes. Inflammatory bowel illness exacerbations. Short digestive tract disorder following medical resections.
Key Elements of Effective Enteral Feeding Training Programs
Training programs need to integrate thorough curricula covering numerous aspects:
1. Composition and Physiology Related to Digestive Health
Understanding exactly how the stomach system functions guarantees specialists can make educated decisions pertaining to feeding methods.
2. Evaluation Skills
Healthcare suppliers need training in assessing indications that dictate whether a client requires enteric or parenteric feeding options.
3. Tube Monitoring Techniques
Learning proper methods for insertion and monitoring reduces threats related to feeding tubes.
4. Monitoring Client Progress
Regular surveillance helps examine nutritional standing while readjusting strategies based on private responses.
FAQs Regarding Enteral and Parenteral Nutrition
1. What is PEG Feeding?
PEG feeding refers specifically to supplying nutrients with a percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy tube inserted straight into the stomach.
2. When ought to I take into consideration using an enteral feed?
Consider making use of an enteric feed when a patient has a practical stomach system but can not consume food by mouth as a result of numerous health issues.

3. What are some usual complications related to PEG feeds?
Common problems consist of infection at the insertion website, tube dislodgment or clog, and goal pneumonia if feeds are not taken care of correctly.
4. The length of time can a specific remain on parenteral nutrition?
Patients can remain on parenteral nutrition indefinitely if very closely kept an eye on; however, long-lasting usage may cause issues like liver damage or nutrient deficiencies.
5. Can enterally fed patients also obtain dental intake?
Yes! Several clients might still eat small amounts by mouth if they have some ingesting ability; this need to constantly be analyzed individually.
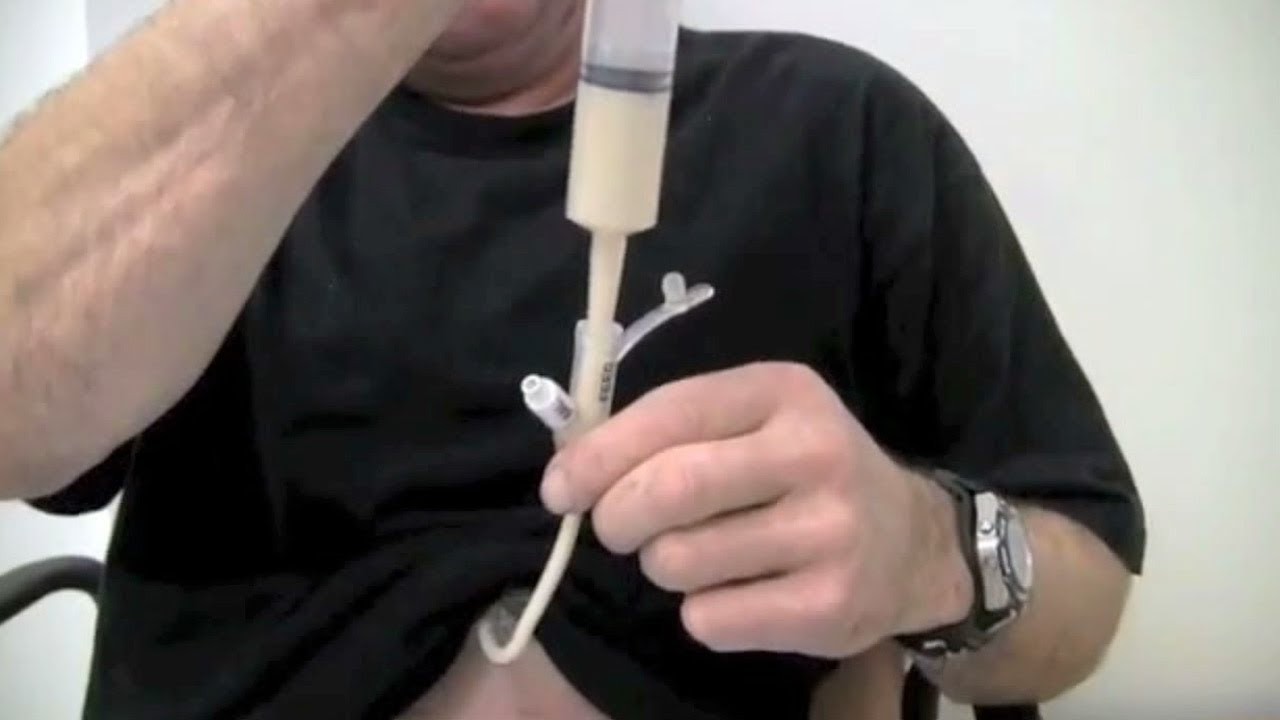
6. What qualifications are offered for specialists taking care of PEG feeds?
Various training courses supply accreditation in PEG feeding techniques consisting of peg feeding training courses comprehensive peg feeding training courses details to Australia that offer important knowledge and skills.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences in between enteral and parenteral nutrition from a training viewpoint is essential for healthcare professionals that aim to supply optimum look after their individuals needing dietary support. Both modalities have distinct applications which highlight their one-of-a-kind roles within professional settings-- ensuring that despite the technique made use of, individuals obtain safe and efficient nutritional therapy tailored to their private needs.